
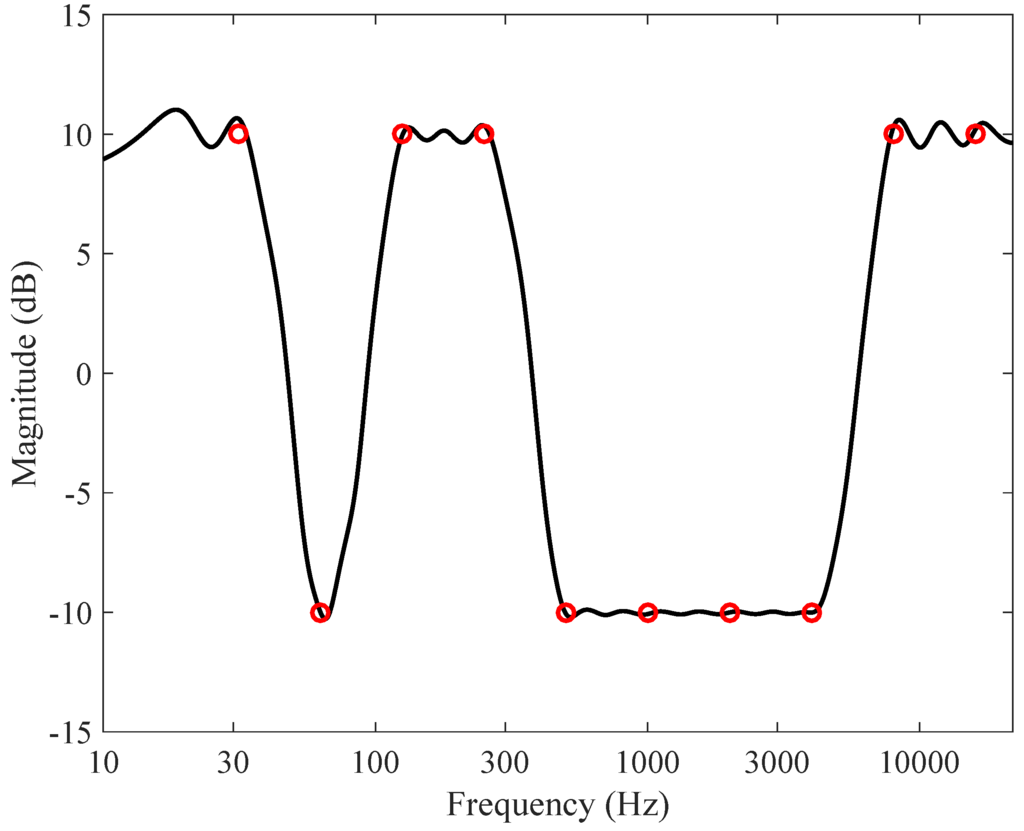
Skilled players can produce tones outside this range. The normal playing range of most three-valved brass instruments extends from three whole tones below the 2nd harmonic of the instrument to the 10th harmonic. Tenor and bass trombone, baritone horn, euphonium, B ♭ horn, bass trumpet, natural trumpet Trumpet, cornet, flugelhorn, soprano trombone This pitch is notated transpositionally as middle C for many of these brass instruments. The following table provides the pitch of the lowest playable resonance (the second harmonic, an octave above the fundamental frequency) and length for some common brass instruments in descending order of pitch. The fundamental is actually missing from the resonances and is impractical to play on some brass instruments, but the overtones account for most pitches. The fundamental frequency of the harmonic series can be varied by adjusting the length of the tubing using the instrument's valve, slide, key or crook system, while the player's embouchure, lip tension and air flow serve to select a specific harmonic from the available series for playing. The combined resonances resemble a harmonic series. The pitch of a brass instrument corresponds to the lowest playable resonance frequency of the open instrument. It's particularly useful for properties of vocal tracks and is used, for example, in software to identify speakers by their voice characteristics.High brass - from the top left: Baroque trumpet in D, modern trumpets in B ♭ and D (same pitch D as Baroque), piccolo trumpet in high B ♭, Flugelhorn in B ♭ right: cornet in B ♭. Cepstrum: The cepstrum of an audio signal is related to the spectrum, but presents the rate of change in the different spectrum bands.By looking at the peaks in the plot, the key frequencies present can be determined even if there is a lot of noise. This gives a small result if the waveform is random (for example, noise) and a large result if it is repetitive (like a musical note). This is repeated for two samples difference and so on, up to the number of samples in the size option. The two copies are then multiplied together, and all the values added up.
This is done by taking two copies of the audio, and moving one forward by one sample. Autocorrelation: These options measure to what extent the sound repeats itself.The amplitudes are normalized such that a 0 dB sine (pure tone) will be (approximately) 0 dB on the graph. Spectrum: (default) - Plots the FFT of the data as described above.Determines what type of processing is done on the audio data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
